The New Security Landscape of Screen Sharing
The increase in remote work has significantly changed how we use screen sharing. It's gone from a handy tool to a critical part of many businesses. But this change has also created new security risks. As we share our screens more, we open up more opportunities for cyberattacks. This makes protecting sensitive information during screen sharing essential.
Traditional security measures, like firewalls and antivirus software, often aren't enough to stop these attacks. These older methods mainly focus on external threats. However, today's threats can come from inside a company, compromised accounts, or clever phishing attacks. We need a better way to secure screen sharing that addresses the risks of sharing sensitive information remotely. The growth of the screen sharing software market highlights this need.
The market was worth about $4.5 billion in 2024, up from $3.2 billion in 2022. This growth is partly due to the rise in remote work, now about 30% of the workforce, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. It's expected to keep growing at a 9.8% CAGR, reaching $10.2 billion by 2033. For more detailed statistics, check out this report: Learn more about the screen sharing software market.
Key Vulnerabilities in Traditional Screen Sharing
Many organizations don't realize the hidden risks in their current screen sharing practices. These risks can be anything from accidentally showing private information to targeted attacks. One common issue is the lack of end-to-end encryption. Without it, anyone intercepting the transmission can see the shared data.
Another problem is weak access controls. If permissions aren't set up correctly, unauthorized people can see sensitive information. Many also forget to set session timeouts. This leaves shared screens open to attack even after the meeting is over.
Addressing the Evolving Threat Landscape
To protect against these threats, we need a multi-layered security approach. This includes using end-to-end encryption to protect data as it's being shared. Strong access controls and detailed permission settings ensure only the right people see the shared content.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of protection. This stops unauthorized access even if login details are stolen. Finally, regular security audits and employee training are essential for staying safe. Together, these measures help businesses navigate the complex world of secure screen sharing. They allow teams to work together efficiently while keeping important data safe.
Non-Negotiable Security Features for Protected Sharing
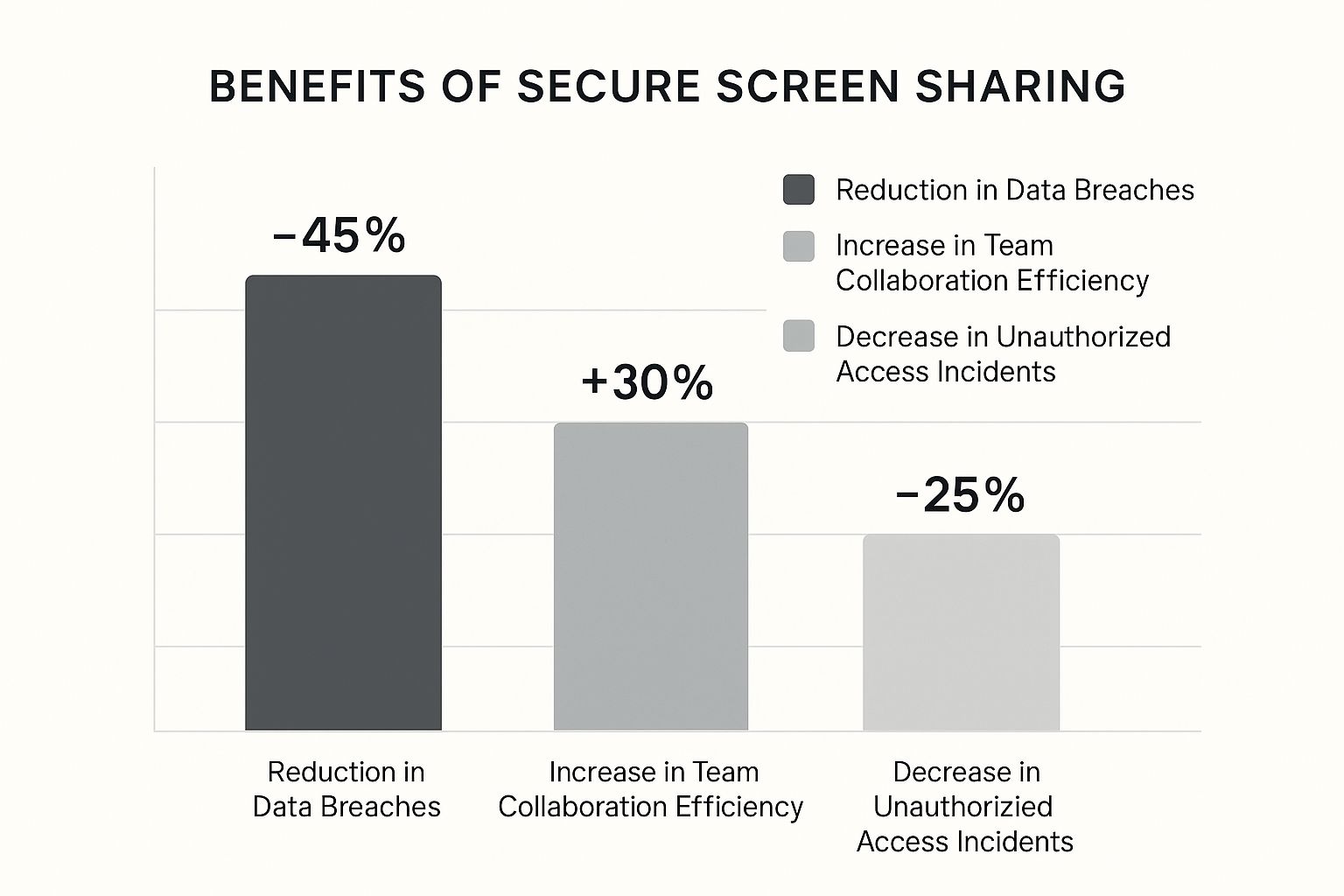
The infographic above illustrates the positive impact of secure screen sharing. It shows how data breaches and unauthorized access are reduced, while team collaboration improves. The data reveals that strong security in your screen sharing practices not only protects sensitive information but also makes teamwork smoother. This leads to fewer security incidents and a boost in productivity. You might also be interested in learning more about visual communication techniques.
This growing need for collaboration demands a renewed focus on security. Simply having screen sharing isn't enough. Those capabilities must be fundamentally secure. This means understanding the essential security features that protect your data and facilitate safe collaboration.
Encryption: Shielding Your Data
The foundation of secure screen sharing is encryption. Think of it as a digital vault for your data. End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is especially important. E2EE makes sure that only the sender and recipient can access the shared information.
This safeguards your data both in transit (as it travels over the internet) and at rest (when stored on servers). Without encryption, your data is vulnerable.
Multi-Factor Authentication: An Extra Layer of Protection
Even with encryption, unauthorized access is still a risk if login credentials are compromised. This is where multi-factor authentication (MFA) becomes essential. MFA requires multiple verification steps, such as a password and a code sent to your phone.
This added layer of security significantly hinders attackers, even if they have your password. MFA is a standard security practice for protecting sensitive accounts and data.
Granular Permission Controls: The Need-to-Know Principle
Secure screen sharing needs more than just controlling who joins a session. Granular permission controls allow administrators to specify what each participant can do. This might involve restricting screen sharing, remote control, or file downloads.
This need-to-know approach minimizes accidental data exposure and contains potential damage from compromised accounts.
To illustrate, imagine a financial presentation. Only specific team members might need access to sensitive financial figures, while others only view the general presentation. This targeted access control protects data while still allowing effective teamwork.
To help you understand the key security features in more detail, we've compiled a comparison table.
The table below, "Essential Security Features Comparison," outlines the critical security features across popular screen sharing platforms and offers a concise overview of their implementation difficulty and overall security impact.
| Security Feature | Description | Implementation Difficulty | Security Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) | Encrypts data so only sender and recipient can decrypt it. | Moderate | High |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple authentication factors for login. | Easy | High |
| Granular Permission Controls | Allows administrators to define specific user permissions. | Moderate | High |
| Session Recording Protection | Prevents unauthorized recording of shared screens. | Varies by platform | Moderate |
| Watermarking | Adds a visual watermark to deter unauthorized sharing of screenshots. | Easy | Low |
Key takeaways from the table: while E2EE, MFA, and granular permissions offer strong security and might require a bit more effort to set up, their impact on data protection is significant. Simpler measures like watermarking are easy to implement but offer limited protection. Choosing the right combination of security features depends on your specific needs and risk tolerance.
Hidden Threats in Screen Sharing (And How to Counter Them)
Beyond obvious risks like unauthorized access, screen sharing sessions face more complex threats that can lead to serious data breaches if ignored. Even seemingly harmless actions can expose sensitive information with potentially devastating consequences. This section explores real-world attack scenarios and offers practical countermeasures.
Accidental Data Leaks: The Unintentional Threat
One of the most common threats isn't intentional, it's accidental. Users may unintentionally reveal sensitive information like passwords, financial data, or private conversations if they don't prepare their screens properly before sharing. Forgetting to close sensitive documents or disable notifications, a seemingly minor oversight, can have significant security implications.
To prevent this, users should always "clean" their desktops before starting a screen share. This involves closing unnecessary applications and removing any sensitive information from view. Disabling notifications also prevents private messages or emails from appearing during the session.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Intercepting the Connection
A more technically sophisticated attack is the man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack. Here, an attacker intercepts the connection between the person sharing their screen and the viewer. If the screen sharing session isn't encrypted, the attacker can see everything being shared.
This type of attack underscores the importance of using screen sharing software with strong security features, particularly end-to-end encryption. Encryption scrambles the data, rendering it unreadable to anyone intercepting it.
Social Engineering: Exploiting Human Trust
Social engineering tactics pose another significant threat. Attackers might impersonate legitimate participants to gain access to a screen sharing session. They might also trick users into sharing sensitive information they wouldn't normally disclose. This highlights the need for strong authentication measures, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), and user training.
Training should focus on recognizing and avoiding social engineering attempts. It should also educate users about the dangers of sharing sensitive information during screen sharing. This education is vital for building a security-conscious culture. Moreover, the demand for secure screen sharing is rising alongside the broader remote access solution market. This market was valued at $2.60 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $8.65 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 19.4%. For more detailed statistics, Explore this topic further. This growth emphasizes the increasing need to incorporate secure screen sharing into broader remote work strategies. By understanding these hidden threats and taking appropriate countermeasures, organizations can ensure their screen sharing practices remain both productive and secure.
Building a Secure Screen Sharing Culture That Works
Technology plays a vital role in secure screen sharing, but it's not the only piece of the puzzle. Even with the most advanced tools, human error can still expose sensitive information. That's why building a security-conscious culture within your organization is so important. This means establishing clear protocols and providing comprehensive training to all users. Fostering a strong security culture also relies on trust; explore effective trust-building activities to strengthen your team's security mindset. This transforms security from a rigid set of rules into a shared responsibility.
Before the Share: Preparation Is Key
Before starting a screen sharing session, a few simple steps can significantly reduce risks. Think of it as tidying up your digital workspace before inviting others in. This desktop preparation acts as your first line of defense.
- Close unnecessary applications: This prevents accidental displays of private information from other programs.
- Clear your desktop: Remove any files or shortcuts containing sensitive data.
- Disable notifications: Prevent private messages, emails, and other alerts from appearing during the session.
These pre-session habits can prevent unintentional data leaks and maintain a professional image.
During the Share: Real-Time Awareness
Once the screen sharing session is underway, real-time awareness is crucial. This means being constantly mindful of the information visible to other participants.
- Share only necessary information: If you only need to share a specific application or document, avoid sharing your entire screen. Utilize the selective sharing features found in many secure screen sharing platforms.
- Verify participant identities: Confirm that all participants are authorized to view the shared content.
- Be mindful of background activity: Even with notifications disabled, unexpected interruptions can happen. Stay aware of your on-screen activity.
These practices help manage potential security risks during active screen sharing, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected.
After the Share: Secure Session Closure
Just as you lock your doors after guests leave, proper post-session security is essential. This is the final step in maintaining a secure screen sharing culture.
- End the session promptly: Don't leave a screen share running unattended. Close the session immediately once it's finished.
- Verify session termination: Double-check that the connection has been completely severed to prevent unauthorized access.
- Log out of the platform: If applicable, log out of the screen sharing platform after each use, especially on shared devices.
These simple post-session practices limit potential vulnerabilities and strengthen your overall security posture.
Tailoring Security to Different Industries
Each industry has unique security challenges and regulatory requirements. Highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance require particularly strict security measures.
The table below, "Secure Screen Sharing Checklist by Industry," provides a quick overview of industry-specific considerations.
| Industry | Regulatory Requirements | Key Security Considerations | Recommended Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | HIPAA | Patient data confidentiality | End-to-end encryption, strict access controls, audit trails |
| Finance | GDPR, PCI DSS | Financial data security, transaction integrity | Multi-factor authentication, data masking, session recording protection |
| Education | FERPA | Student privacy | Limited screen sharing, parental consent, content filtering |
Tailoring your security practices to specific industry needs helps ensure compliance and effectively protects sensitive data. This approach balances stringent security with the need for efficient collaboration.
Selecting Secure Screen Sharing Tools That Match Your Risk Profile
The market is flooded with screen sharing tools, each promising top-notch security. However, not all live up to these claims. This section offers a practical framework for evaluating these tools, going beyond surface-level features to examine the underlying security infrastructure. For more on remote IT support tools, check out this helpful resource: How to master remote IT support tools. This guide will assist you in making smart decisions about choosing tools that fit your needs.
Beyond the Checkboxes: Evaluating True Security
When choosing a secure screen sharing tool, don't simply rely on the advertised features. Delve deeper into the platform's architecture and security practices. Start by considering compliance certifications. Does the tool adhere to relevant industry standards, such as HIPAA for healthcare or GDPR for data privacy? These certifications demonstrate a commitment to protecting sensitive information.
Also, investigate their vulnerability management processes. How does the vendor handle identified security flaws? A robust system for identifying and patching vulnerabilities is essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
Finally, the architectural approach itself matters. Is security integrated into the platform's core design, or is it a tacked-on afterthought? A proactive security design, built from the ground up, provides a more resilient foundation.
Implementation, Integration, and Cost: Practical Considerations
Beyond security features, practical considerations play a significant role. How easy is the tool to implement? A complicated setup process can create security vulnerabilities and hinder user adoption.
Consider the tool's integration capabilities. Will it seamlessly integrate with your existing security infrastructure, including firewalls and authentication systems? Smooth integration simplifies management and strengthens your overall security posture.
Finally, remember the total cost of ownership. This includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance, support, and potential training expenses. Balancing security needs with budgetary constraints is key for long-term success.
Tailoring Your Choice to Your Risk Profile
Not all organizations have identical security needs. A small startup will have different requirements than a large financial institution. Therefore, aligning your tool selection with your specific risk profile is critical.
Here are some key factors to consider:
- Organization Size: Larger organizations typically need more robust security features and granular controls.
- Industry Requirements: Highly regulated industries, like healthcare and finance, face stricter compliance obligations.
- Specific Risk Factors: Organizations handling highly sensitive data require more stringent security measures.
By carefully weighing these factors, you can choose a secure screen sharing solution that provides the right level of protection without undue complexity or cost. This tailored approach ensures your screen sharing practices meet your organization's unique security and compliance needs.
Advanced Technical Safeguards for Maximum Protection
For organizations handling sensitive data or facing significant security threats, basic secure screen sharing features just aren't enough. It's essential to go beyond standard practices and implement advanced technical safeguards to create truly protected sharing environments. Let's explore how security professionals build these fortress-like environments.
Network Segmentation: Isolating Screen Sharing Traffic
One powerful technique is network segmentation. This isolates screen sharing traffic onto a dedicated network segment. Think of it as a separate highway lane exclusively for screen sharing data. This isolation prevents unauthorized access from other parts of the network and contains potential breaches.
For instance, if one part of the network is compromised, the segmented screen sharing traffic remains safe.
Endpoint Hardening: Securing the Devices Themselves
Endpoint hardening focuses on securing the devices used for screen sharing. This involves configuring devices with strict security settings to minimize vulnerabilities. This could include disabling unnecessary services, enforcing strong password policies, and regularly updating software to patch security holes. Hardening endpoints is like reinforcing the doors and windows of your house, making it much tougher for attackers to break in.
When choosing secure screen sharing tools, make sure they adhere to industry best practices. Learn more about selecting compliant tools with these regulatory compliance solutions.
Advanced Monitoring: Detecting Suspicious Activity
Using sophisticated monitoring systems helps organizations detect unusual screen sharing activity that could signal a security breach. These systems can track login attempts, monitor data transfers, and flag suspicious actions like unusual file access or unexpected screen sharing requests. This real-time monitoring acts like a security camera, alerting you to potential issues early on.
Zero Trust, Data Loss Prevention, and Security Testing: A Multi-Layered Approach
A zero-trust architecture for screen sharing provides an additional layer of security. This framework assumes no user or device is inherently trustworthy and requires verification at every access point, lessening the impact of compromised credentials. For further information on secure system implementation, you might find this helpful: How to master technical documentation.
Data loss prevention (DLP) configurations designed for screen sharing can prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization. DLP systems can identify and block the sharing of confidential data, like credit card numbers or personal health information, even during screen sharing sessions. Finally, regular security testing of your screen sharing environment is critical. This could include penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses.
By combining these advanced technical safeguards, organizations can create incredibly strong security around their screen sharing practices, protecting sensitive information even in high-risk environments.
The Future of Secure Screen Sharing: What's Coming Next
Secure screen sharing is constantly evolving. It must adapt to new challenges and incorporate the latest technology. This evolution is driven by the need to protect sensitive data in an increasingly connected world. Let’s explore some key innovations shaping the future of this important technology.
AI-Powered Threat Detection: The Rise of Intelligent Security
Artificial intelligence (AI) is set to change security within screen sharing platforms. AI algorithms can analyze screen sharing sessions live, looking for unusual activity that might suggest a security risk. For example, AI could detect unauthorized access to sensitive files or unusual keyboard activity hinting at a compromised account.
This proactive approach enables faster responses to potential breaches, reducing the impact of any attacks. Furthermore, AI can adapt and learn, improving its effectiveness at identifying and stopping new threats over time. This makes AI a powerful tool in the fight against cybercrime.
Zero Trust Architectures: Reinventing the Security Framework
Zero trust is a security model based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It requires authentication and authorization at every step, regardless of a user's location – inside or outside the network. This limits the damage from compromised logins or insider threats.
For secure screen sharing, zero trust means verifying each participant's identity and access rights before they can view or interact with the shared screen. Even during the session, accessing specific files or features could require further verification. This added security offers strong protection.
Quantum-Resistant Encryption: Preparing for the Future of Cryptography
Quantum computing poses a challenge to current encryption. However, quantum-resistant encryption is being developed to tackle this. This type of encryption uses complex mathematical algorithms designed to withstand attacks from quantum computers. While quantum computing is still developing, adopting quantum-resistant encryption now will help ensure screen sharing remains secure as technology advances.
This forward-thinking approach protects information now and prepares for the future of cybersecurity. Investing in quantum-resistant encryption future-proofs your screen sharing strategy.
The Impact of Regulation: Shaping Development and Best Practices
Data privacy regulations, like GDPR, influence how secure screen sharing platforms are built. These regulations often require specific security measures such as strong encryption and robust data governance policies. This external pressure leads to the development of innovative security features and pushes stronger security standards across various industries. Staying informed about these regulations is vital for selecting compliant tools and using effective security practices.
By understanding these emerging trends and preparing for the future of security, you can make smart decisions about your screen sharing tools and practices. This will help ensure your virtual collaborations remain both productive and secure.
Ready to experience the future of secure screen sharing? Try Screendesk today and discover how its advanced features protect your data and enhance collaboration.