Demystifying Customer Experience Journey Mapping
Customer experience journey mapping is more than just a popular concept; it's a valuable tool for understanding how customers interact with your business. It visually represents every touchpoint a customer has with your brand, from initial awareness to, ideally, long-term loyalty. This visualization goes beyond simply charting the steps; it explores customer motivations, pain points, and emotions at each stage.
Understanding the Power of Visualization
Think of it like planning a road trip. A traditional map shows the route, but a customer journey map is like a detailed travel guide. It highlights not only the roads, but also points of interest, potential traffic jams, and the best rest stops. This comprehensive view allows businesses to identify key moments to improve the customer experience and build stronger connections. For example, if a customer struggles to navigate your website, they might abandon their purchase. A well-placed help button or chatbot could provide assistance and save the sale.
Why Traditional Mapping Falls Short
Traditional customer mapping often focuses only on the transactional aspects of the customer journey. However, today's customers expect more than just efficient transactions; they want personalized, meaningful experiences. This is where customer experience journey mapping shines. By incorporating emotional data, businesses gain deeper insights into customer behavior and identify opportunities to exceed expectations. This shift from transaction-focused to experience-centered mapping is why companies are seeing significant improvements in customer loyalty.
The Growing Importance of Customer Experience
Customer journey mapping is increasingly important as businesses work to enhance customer experience. By 2025, 91% of businesses want to be customer experience leaders in their sectors. This highlights the importance of creating a positive customer experience, which is crucial for business success. Furthermore, 88% of decision-makers emphasize customizing these experiences, although they often lack the resources. This emphasis on customer experience is further shown by the fact that 63% of CX decision-makers report its growing importance. You can find more detailed statistics here: Learn more about customer journey mapping statistics.
Key Components of an Effective Journey Map
Several components create a truly effective customer journey map:
- Customer Personas: Detailed descriptions of your ideal customer, including demographics, motivations, and pain points.
- Touchpoints: All the interaction points a customer has with your brand, from your website and social media to customer service.
- Emotional Journey: Tracking how customers feel at each stage helps pinpoint moments of delight and frustration.
- Pain Points and Opportunities: Identifying areas where the customer experience can be improved.
By combining these elements, businesses create a dynamic plan for delivering exceptional customer experiences and driving long-term growth. This allows for a more proactive and empathetic approach to customer service, fostering stronger relationships and increased brand loyalty.
The Evolution From Simple Maps to Experience Ecosystems
Customer journey mapping has evolved significantly. These maps were once simple, linear flowcharts of basic customer interactions. This older method is no longer effective in today's dynamic marketplace. This evolution reflects a change in how businesses understand and interact with their customers.
From Linear Flows to Dynamic Interactions
Early customer journey maps often resembled basic service blueprints, primarily focused on internal company processes. They outlined touchpoints in a simple, sequential manner. This method was sufficient when customer interactions were predictable and generally happened within a single channel. For instance, a customer might enter a store, browse, talk to a salesperson, and purchase, all in one visit.
The Rise of the Omnichannel Customer
This linear model no longer reflects modern customer behavior. Customers interact with businesses across many touchpoints, both online and offline, switching between them seamlessly. They might research online, compare prices on an app, visit a store to see the product, then purchase online later. This omnichannel behavior necessitates a more nuanced approach to customer experience journey mapping. Learn more about creating a seamless experience: How to master the omnichannel experience.
The Importance of Adaptability and Real-Time Data
The complexity of these journeys has made traditional methods ineffective. Recent studies show that customer journeys need intelligent design and dynamic management, supported by real-time data. This shift is essential for creating connected digital experiences that satisfy customer expectations. In fact, 73% of customers use multiple channels during their shopping experience. To tackle these challenges, many businesses are using advanced analytics and AI to improve customer journey mapping and the overall customer experience. For a deeper look at customer journey success, see: Discover more insights about customer journey success.
Mapping the Experience Ecosystem
Today's customer experience journey mapping focuses on the entire ecosystem of a customer's interaction with a brand. New to process mapping? Start with the basics: Demystifying SOPs and Work Instructions. This comprehensive approach includes:
- Mapping Non-Linear Journeys: Recognizing that customers don’t always follow a predictable path.
- Incorporating Emotional Data: Understanding how customers feel at every touchpoint is crucial.
- Utilizing Technology: Leveraging software and data analytics to capture and analyze multi-channel interactions.
By transforming customer experience journey mapping from simple diagrams to dynamic, data-driven tools, businesses can better meet the needs of today's consumers. This leads to exceptional experiences that build loyalty and drive growth.
Building Journey Maps That Drive Real Action
What separates a customer journey map that gets ignored from one that actually helps a business grow and change? The key is in the specifics. An effective customer journey map isn't just a pretty picture; it's a strategic business tool. It combines creative thinking with data-driven analysis, capturing both the emotional side and the practical interactions of the customer experience.
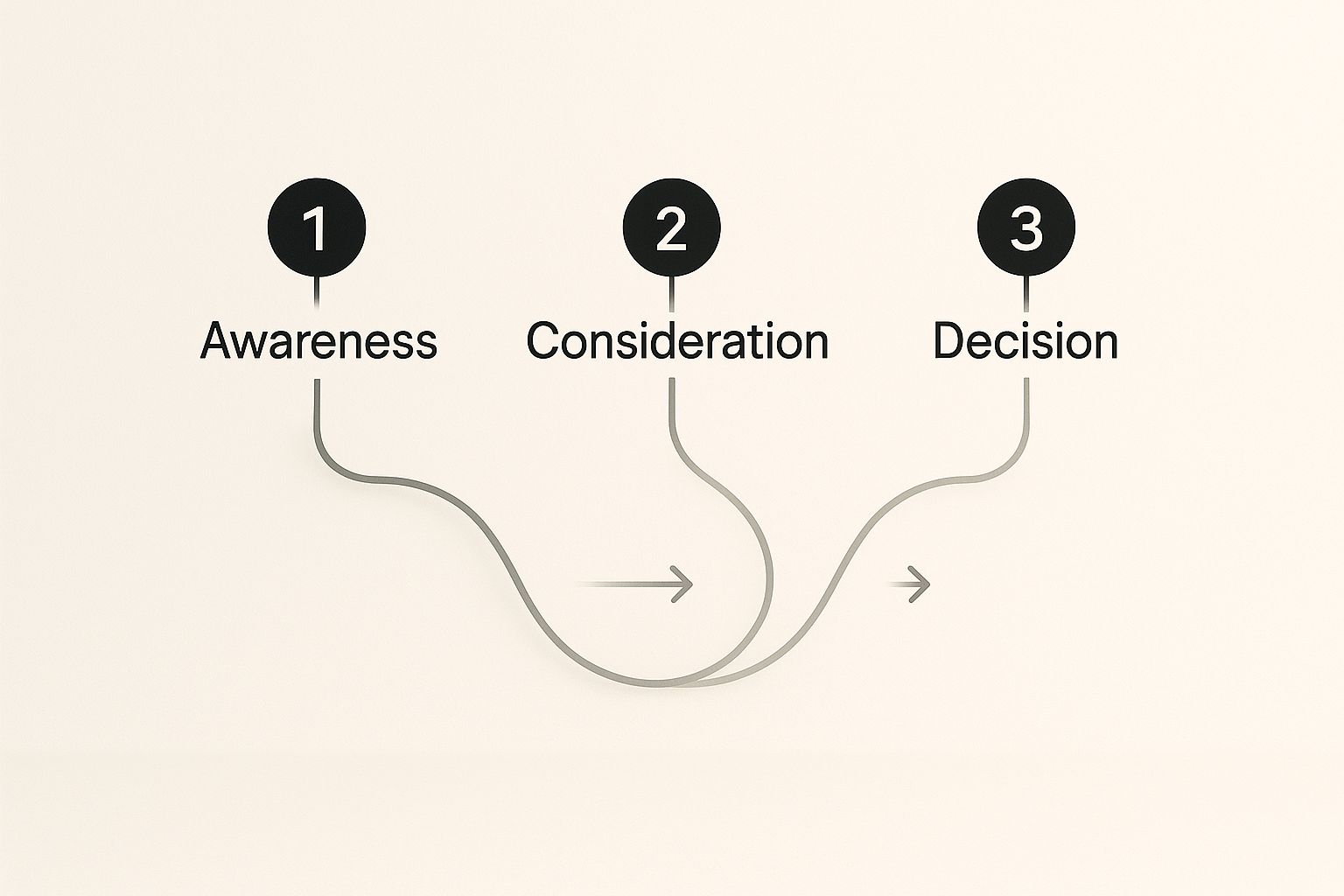
This infographic shows a simplified customer journey with three main phases: Awareness, Consideration, and Decision. Each stage is a key step the customer takes before buying something. The connected path shows how important a smooth transition between these stages is for a positive overall experience. This simple visual demonstrates how crucial it is for businesses to nurture the customer relationship at each point in their journey.
Essential Components of an Effective Journey Map
Several important elements contribute to a truly useful journey map. For example, well-defined customer personas are essential. These detailed profiles provide a deep understanding of your target audience's needs, motivations, and behaviors, going beyond simple demographics. This allows you to customize the journey map for specific customer groups. Clear engagement phases bring structure to the journey map, breaking it down into manageable stages. This helps businesses understand where the customer is mentally at each step.
To understand this further, let's look at some key components:
-
Touchpoints: These are all the interactions a customer has with your brand. From visiting your website to contacting customer service, every touchpoint shapes their experience.
-
Emotional Responses: Understanding how customers feel at each touchpoint is just as important as understanding what they do. This means paying attention to both positive and negative emotions.
-
Improvement Opportunities: This is where the real work begins. A good journey map not only highlights the problems, but also offers potential solutions. These should be specific and actionable.
To further illustrate this, let's look at the following table:
Journey Mapping Components That Drive Results
This comparison examines critical elements every effective journey map should include, revealing their strategic purpose and implementation considerations.
| Component | Strategic Value | Implementation Approach | Common Pitfalls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Personas | Deeply understand target audience needs and motivations | Research, interviews, data analysis | Relying on assumptions, lack of segmentation |
| Engagement Phases | Structure the journey into digestible stages | Map key steps in the customer lifecycle | Overly complex phases, misaligned with customer behavior |
| Touchpoints | Identify all interaction points with the brand | Customer journey analysis, website analytics | Missing crucial touchpoints, focusing only on digital interactions |
| Emotional Responses | Understand customer feelings at each stage | Qualitative research, sentiment analysis | Neglecting negative emotions, misinterpreting feedback |
| Improvement Opportunities | Pinpoint areas for enhancing the customer experience | Brainstorming, prioritize solutions based on impact | Lack of actionable steps, failure to implement changes |
As this table demonstrates, building an effective customer journey map requires careful consideration of several crucial elements.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Many customer journey maps end up being ineffective because they fall into common traps. One major mistake is a lack of focus. Trying to map every single customer journey at once can create a confusing and overwhelming document. Instead, focus on specific customer segments or journeys. Another common mistake is relying only on internal guesses instead of real customer data. Getting feedback through surveys, interviews, and website analytics tools like Google Analytics is crucial for creating an accurate map. Lastly, not acting on the insights gathered is a huge wasted opportunity. A journey map should be a dynamic tool, continuously being updated and used to inform business decisions.
Practical Frameworks and Templates
You don't need a team of consultants or expensive software to create effective journey maps. Simple frameworks, like the infographic shown above, offer a good starting point. Many free templates available online can be adapted to your specific business needs. These resources help you get started quickly and easily. By following best practices and focusing on the essential components, you can build customer journey maps that drive real, tangible results. For more insights on the impact of CX on your bottom line, check out this article: How to measure the ROI of customer experience.
Gathering Insights That Actually Reflect Reality
Many customer experience journey maps miss the mark because they're built on assumptions, not real-world data. This makes gathering accurate insights essential for a successful process. To really understand the customer experience, we need to move past guesswork and dive into the actual behaviors and feelings of our customers. This section explores different research methods that can help uncover those authentic experiences.
Research Methods for Authentic Insights
Several research methods can help us gather authentic insights for customer experience journey mapping. For example, customer shadowing involves observing customers as they interact with your product or service. This provides firsthand insight into their behaviors and challenges.
Depth interviews allow for a deeper understanding of individual customer experiences. By asking open-ended questions, you can uncover their motivations, pain points, and unmet needs. To truly understand customer needs during your journey mapping process, consider using samples of open-ended questions.
Beyond these qualitative methods, quantitative approaches also offer valuable data. Digital analytics tools like Google Analytics can track website behavior, providing insights into how customers navigate your online platforms. This data can reveal areas for improvement in your website design and user experience.
Social listening involves monitoring social media channels and online forums to understand what customers are saying about your brand. This can provide valuable feedback on product features, customer service, and overall brand perception.
Selecting the Right Approach
The best research methods for your customer experience journey mapping will depend on your specific goals and resources. For a quick overview of customer sentiment, social listening might be sufficient.
However, for a deeper understanding of customer needs, depth interviews or customer shadowing might be more appropriate. Often, a combination of methods provides the most complete picture.
Overcoming Confirmation Bias
One challenge in customer research is confirmation bias, the tendency to look for information that confirms pre-existing beliefs. This can lead to inaccurate results and missed opportunities for improvement.
To mitigate this, it's important to approach research with an open mind and actively seek out diverse perspectives. This includes interviewing customers with both positive and negative experiences.
Involving different team members in the research process can also help minimize individual biases.
Ethical Considerations and Accessing Hard-to-Reach Segments
It's crucial to conduct research ethically, respecting customer privacy and obtaining informed consent. This is especially important when dealing with sensitive data or vulnerable customer segments.
Accessing hard-to-reach segments can also be a challenge. Reaching customers who have churned, for example, might require specific outreach strategies like targeted email campaigns or partnerships with relevant organizations. By carefully considering these factors, you can improve the accuracy and depth of your customer experience journey mapping, leading to more valuable insights.
Transforming Insights Into Experience Improvements
Creating a beautiful customer journey map is only the first step. The real value lies in using those insights to implement actual improvements. This means translating the visual representation of your customer's journey into concrete actions. These actions should enhance their experience and ultimately benefit your business.
Prioritizing Improvements for Maximum Impact
After identifying areas for improvement, the next step is prioritization. Not all improvements are created equal. Some offer quick wins with minimal effort, while others require more significant investment and time. A good strategy is to focus on high-impact, low-effort improvements first.
These quick wins generate momentum and demonstrate the value of customer journey mapping to stakeholders. For example, simplifying a complex online checkout process could be a high-impact, low-effort improvement. This change could significantly reduce cart abandonment rates and increase conversions.
Communicating and Aligning Teams Around the Customer
Effective communication is crucial for turning insights into action. Journey mapping findings should be shared across all relevant teams. This breaks down silos and fosters a customer-centric culture. This shared understanding ensures everyone is working towards the same goal: improving the customer experience.
Visual presentations, workshops, and storytelling are effective ways to communicate these findings and engage teams. Securing executive buy-in is essential for larger initiatives. Presenting a clear business case that links customer experience improvements to key business metrics – like increased revenue or reduced churn – will help gain support. You might be interested in: How to measure the ROI of customer experience.
Measuring the Impact and Creating Feedback Loops
Establishing clear metrics is critical for measuring the success of implemented changes. These metrics should align with the initial objectives of the customer journey mapping process. For instance, if the goal was to reduce customer effort, metrics like task completion time or customer service call volume could be tracked.
Creating feedback loops is also vital for continuous refinement. This means regularly gathering customer feedback and using it to update the journey map and identify new areas for improvement. This iterative approach ensures the journey map remains a dynamic and valuable tool.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
The ultimate goal of customer journey mapping is to create a culture of continuous improvement centered around the customer. This requires ongoing effort and commitment from all teams. By embedding customer-centric thinking into every aspect of the business, organizations can create experiences that not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
This leads to increased loyalty, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and sustainable business growth. To truly understand customer needs, consider using samples of open ended questions during your journey mapping process. This can help gather richer qualitative data and uncover hidden pain points. By actively seeking feedback and iteratively improving the customer journey, businesses can build stronger relationships and achieve long-term success.
Mastering Multi-Channel and Personalized Journeys
Customer journeys are becoming more complex. At the same time, the demand for personalized experiences is increasing. This means customer experience journey mapping needs to evolve. We need to go beyond basic, linear journeys and embrace the many ways customers interact with businesses. This section explores advanced techniques for mapping these more sophisticated journeys. We'll focus on how to deliver personalized interactions effectively.
Mapping Non-Linear Journeys
Traditional journey maps often show a straight line from awareness to purchase. However, today’s customer journeys rarely follow such a predictable path. Customers interact with brands across many touchpoints. These include websites, social media, email, and physical stores. Customers often switch between these touchpoints many times before making a purchase.
This non-linear behavior requires a different mapping approach. We need a way to represent the interconnected loops and decision points. Think of it like a "choose your own adventure" book. Each choice leads to a different page, and maybe even a different ending. A customer clicking on a social media ad might have a very different experience than a customer who finds your website through a search engine.
Incorporating Digital Touchpoints and Personalization
This multi-channel reality means including digital touchpoints, AI interactions, and real-time personalization in our maps. For example, imagine a customer using your mobile app. They receive a personalized product recommendation based on their browsing history. This interaction should be included in the journey map because it influences their experience. But simply adding every possible touchpoint can make the map too complicated. Focus on the most important interactions and the emotional responses they create.
Mapping for Personalization at Scale
Providing personalized experiences at scale takes a strategic approach to customer experience journey mapping. This means understanding the different customer segments and adapting the journey map accordingly.
- Identify Key Segments: Group customers based on similar characteristics, needs, and behaviors.
- Map Unique Journeys: Create separate journey maps for each segment. Highlight their specific needs and pain points.
- Personalize Touchpoints: Design touchpoints to provide customized content and experiences based on the needs of each segment.
Segmenting your audience lets you personalize the journey map. This makes it more relevant to the specific audience it represents. This focused approach creates more meaningful experiences, and ultimately, builds customer loyalty. Learn more in our article about How to Increase Customer Retention.
Practical Approaches and Actionable Outputs
Even with the added complexity of multi-channel and personalized journeys, it’s important to create useful outputs. One way is to map emotional journeys alongside functional journeys. This means tracking not only the steps a customer takes but also their feelings at each stage. This added emotional insight can reveal important moments of delight or frustration that influence their decisions.
Visualizing these emotional responses helps you identify areas where improvements will have the biggest impact on customer satisfaction. By combining emotional and functional journeys, your customer experience journey map becomes a powerful tool for creating positive change within your organization.
To understand the various approaches to journey mapping, let's look at a comparison table. This table summarizes the key differences between traditional and multi-channel techniques.
Multi-Channel Journey Mapping Approaches
This comparison reveals the key differences between traditional and advanced journey mapping methodologies, highlighting practical tools and outcomes.
| Approach Element | Traditional Methods | Multi-Channel Techniques | Implementation Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Linear customer journey | Non-linear, multi-platform interactions | Integrating data from various touchpoints |
| Touchpoints | Limited, often siloed | Integrated, across online and offline channels | Requires cross-departmental collaboration |
| Data Sources | Primarily qualitative (e.g., interviews, surveys) | Combines qualitative and quantitative data (e.g., web analytics, CRM) | Data integration and analysis tools are essential |
| Personalization | Limited or non-existent | Highly personalized based on customer segments and individual behaviors | Leveraging customer data platforms and personalization engines |
| Outputs | Static journey maps | Dynamic, interactive dashboards and visualizations | Ongoing monitoring and optimization |
By analyzing this table, we can clearly see the advantages of multi-channel journey mapping. It offers a more comprehensive and nuanced view of the customer experience. This deeper understanding is crucial for delivering truly personalized and effective customer experiences.
The Future of Customer Experience Journey Mapping
Customer experience journey mapping is constantly evolving. As technology changes and customer expectations shift, businesses need to adapt their mapping strategies to stay ahead of the curve. This section explores some key trends shaping the future of customer experience journey mapping.
Predictive Journey Mapping With AI and Machine Learning
Imagine knowing what a customer needs before they even realize it. That’s the power of predictive journey mapping. Using AI and machine learning, businesses can analyze large amounts of customer data to uncover patterns and predict future actions. This allows for proactive support and more personalized experiences.
For example, if the data suggests a customer might abandon their online shopping cart, a well-timed email offering a discount or free shipping could make all the difference. This approach shifts customer experience journey mapping from reactive to predictive.
Real-Time Data Integration and Living Visualizations
Static journey maps are quickly becoming outdated. Real-time data integration is turning these maps into living visualizations that accurately reflect the current customer experience. By linking journey maps to live data streams, businesses can observe customer interactions in real time.
This offers immediate insights into new trends and potential issues. For example, a sudden increase in negative social media comments about a new product feature could trigger an immediate review and corrective action. This real-time responsiveness allows for quick adjustments and continuous improvement.
Immersive Technologies and Employee Empathy
One of the greatest challenges in customer experience journey mapping is building empathy among employees. Immersive technologies, like Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), are helping to bridge this gap. By recreating the customer journey, these technologies let employees experience the process firsthand, from the customer’s perspective.
Imagine a customer support representative using VR to navigate a confusing section of a website. This type of hands-on experience cultivates a deeper understanding of customer frustrations and encourages more empathetic responses.
Connecting Employee and Customer Journeys
The employee experience and the customer experience are deeply connected. Satisfied employees are much more likely to provide excellent customer service. This connection has led to a growing emphasis on linking employee journey mapping with customer experience journey mapping.
By understanding the employee journey, businesses can identify pain points that impact their ability to deliver top-notch customer service. For instance, if employees struggle with outdated software, it can lead to longer wait times and unhappy customers. Addressing these internal hurdles improves both employee satisfaction and the customer experience. This interconnected approach recognizes that a positive employee experience often translates to a positive customer experience.
Ready to enhance customer support with video solutions? Learn more about how Screendesk can improve your workflow and elevate your customer experience.